剑指Offer面试题:27.最小的k个数
一、题目:最小的k个数
题目:输入n个整数,找出其中最小的k个数。例如输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。
这道题是典型的TopK问题,其最简单的思路莫过于把输入的n个整数排序,排序之后位于最前面的k个数就是最小的k个数。这种思路的时间复杂度是O(nlogn),但是面试官会要求时间复杂度保持在O(n)。
二、解题思路
2.1 需要修改数据源的O(n)解法
基于快速排序中的Partition函数来解决这个问题。如果基于数组的第k个数字来调整,使得比第k个数字小的所有数字都位于数组的左边,比第k个数字大的所有数字都位于数组的右边。这样调整之后,位于数组中左边的k个数字就是最小的k个数字(这k个数字不一定是排序的)。
But,采用这种思路是有限制的。我们需要修改输入的数组,因为函数Partition会调整数组中数字的顺序。
2.2 适合处理海量数据的O(nlogk)解法
可以先创建一个大小为k的数据容器来存储最小的k个数字,接下来我们每次从输入的n个整数中读入一个数。
如果容器中已有的数字少于k个,则直接把这次读入的整数放入容器之中;
如果容器中已有k个数字了,也就是容器已满,此时我们不能再插入新的数字而只能替换已有的数字。
找出这已有的k个数中的最大值,然后拿这次待插入的整数和最大值进行比较。如果待插入的值比当前已有的最大值小,则用这个数替换当前已有的最大值;如果待插入的值比当前已有的最大值还要大,那么这个数不可能是最小的k个整数之一,于是我们可以抛弃这个整数。
因此当容器满了之后,我们要做3件事情:一是在k个整数中找到最大数;二是有可能在这个容器中删除最大数;三是有可能要插入一个新的数字。如果用一个二叉树来实现这个数据容器,那么我们能在O(logk)时间内实现这三步操作。因此对于n个输入数字而言,总的时间效率就是O(nlogk)。
根据以上步骤,这里采用C#实现代码如下:(采用了红黑树结构作为容器,当然也可以采用堆来实现,有关红黑树的细节可以阅读yangecnu的《浅谈算法和数据结构之红黑树》)
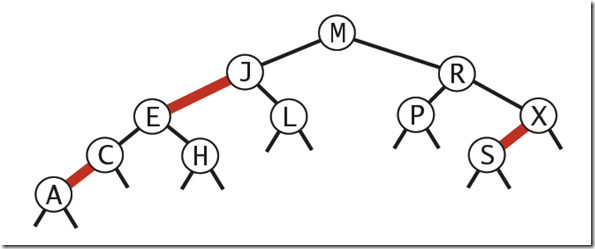
public static void GetLeastNumbersByRedBlackTree(List<int> data, SortedDictionary<int, int> leastNumbers, int k) { leastNumbers.Clear(); if (k < 1 || data.Count < k) { return; } for (int i = 0; i < data.Count; i++) { int num = data[i]; if (leastNumbers.Count < k) { leastNumbers.Add(num, num); } else { int greastNum = leastNumbers.ElementAt(leastNumbers.Count - 1).Value; if (num < greastNum) { leastNumbers.Remove(greastNum); leastNumbers.Add(num, num); } } } }
此解法虽然要慢一点,但它有两个明显的优点:
一是没有修改输入的数据(代码中的变量data)。我们每次只是从data中读入数字,所有的写操作都是在容器leastNumbers中进行的。
二是该算法适合海量数据的输入(包括百度在内的多家公司非常喜欢与海量输入数据相关的问题)。
假设题目是要求从海量的数据中找出最小的k个数字,由于内存的大小是有限的,有可能不能把这些海量的数据一次性全部载入内存。这个时候,我们可以从辅助存储空间(比如硬盘)中每次读入一个数字,根据GetLeastNumbers的方式判断是不是需要放入容器leastNumbers即可。
这种思路只要求内存能够容纳leastNumbers即可,因此它最适合的情形就是n很大并且k较小的问题。
三、单元测试
3.1 测试用例
(1)封装辅助测试方法TestPortal()
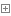
public static void TestPortal(string testName, int[] data, int[] expected, int k) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(testName)) { Console.WriteLine("{0} begins:", testName); } Console.WriteLine("Result for solution:"); if (expected != null) { Console.WriteLine("Expected result:"); for (int i = 0; i < expected.Length; i++) { Console.Write("{0}\t", expected[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); } if(data == null) { return; } List<int> dataList = new List<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++) { dataList.Add(data[i]); } SortedDictionary<int, int> leastNumbers = new SortedDictionary<int, int>(); GetLeastNumbersByRedBlackTree(dataList, leastNumbers, k); Console.WriteLine("Actual result:"); foreach (var item in leastNumbers) { Console.Write("{0}\t", item.Value); } Console.WriteLine("\n"); }
(2)功能测试、特殊输入测试
// k小于数组的长度 public static void Test1() { int[] data = { 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8 }; int[] expected = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; TestPortal("Test1", data, expected, expected.Length); } // k等于数组的长度 public static void Test2() { int[] data = { 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8 }; int[] expected = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }; TestPortal("Test2", data, expected, expected.Length); } // k大于数组的长度 public static void Test3() { int[] data = { 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8 }; int[] expected = null; TestPortal("Test3", data, expected, 10); } // k等于1 public static void Test4() { int[] data = { 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8 }; int[] expected = { 1 }; TestPortal("Test4", data, expected, expected.Length); } // k等于0 public static void Test5() { int[] data = { 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8 }; int[] expected = null; TestPortal("Test5", data, expected, 0); } // 数组中有相同的数字 public static void Test6() { int[] data = { 4, 5, 1, 6, 2, 7, 2, 8 }; int[] expected = { 1, 2 }; TestPortal("Test6", data, expected, expected.Length); } // 输入空指针 public static void Test7() { TestPortal("Test7", null, null, 0); }
3.2 测试结果
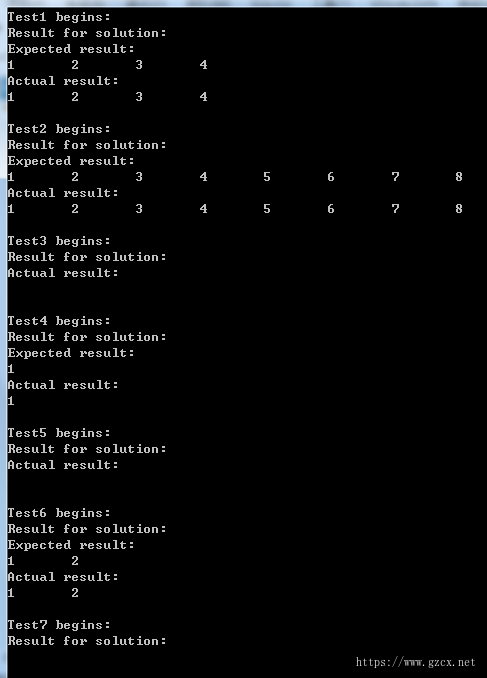
四、分布式计算
4.1 Hadoop MapReduce简单介绍
Hadoop MapReduce是一个软件框架,基于该框架能够容易地编写应用程序,这些应用程序能够运行在由上千个商用机器组成的大集群上,并以一种可靠的,具有容错能力的方式并行地处理上TB级别的海量数据集。
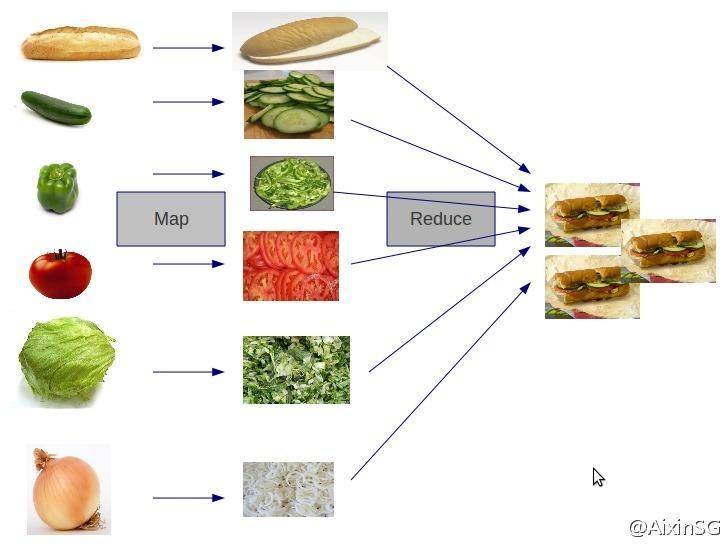
因此,对于MapReduce,可以简洁地认为,它是一个软件框架,海量数据是它的“菜”,它在大规模集群上以一种可靠且容错的方式并行地“烹饪这道菜”。
4.2 使用MapReduce解决TopK问题
这里我们使用一个随机生成的100万个数字的文件,也就是说我们要做的就是在100万个数中找到最大的前100个数字。
实验数据下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qWt4WaS
(1)map函数

public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, LongWritable> { public static final int K = 100; private TreeMap<Long, Long> tm = new TreeMap<Long, Long>(); protected void map( LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { try { long temp = Long.parseLong(value.toString().trim()); tm.put(temp, temp); if (tm.size() > K) { tm.remove(tm.firstKey()); // 如果是求topk个最小的那么使用下面的语句 //tm.remove(tm.lastKey()); } } catch (Exception e) { context.getCounter("TopK", "errorLog").increment(1L); } }; protected void cleanup( org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { for (Long num : tm.values()) { context.write(NullWritable.get(), new LongWritable(num)); } }; }
其中,使用了java中的红黑树对应的数据结构TreeMap类,cleanup()方法是在map方法结束之后才会执行的方法,这里我们将在该map任务中的前100个数据传入reduce任务中;
(2)reduce函数

public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable> { public static final int K = 100; private TreeMap<Long, Long> tm = new TreeMap<Long, Long>(); protected void reduce( NullWritable key, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> values, Reducer<NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { for (LongWritable num : values) { tm.put(num.get(), num.get()); if (tm.size() > K) { tm.remove(tm.firstKey()); // 如果是求topk个最小的那么使用下面的语句 //tm.remove(tm.lastKey()); } } // 按降序即从大到小排列Key集合 for (Long value : tm.descendingKeySet()) { context.write(NullWritable.get(), new LongWritable(value)); } }; }
在reduce方法中,依次将map方法中传入的数据放入TreeMap中,并依靠红黑色的平衡特性来维持数据的有序性。
(3)完整代码

package algorithm; import java.net.URI; import java.util.TreeMap; import mapreduce.MyWordCountJob.MyMapper; import mapreduce.MyWordCountJob.MyReducer; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.CompressionCodec; import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec; import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TestJobCounters.NewIdentityReducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner; import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool; import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner; public class MyTopKNumJob extends Configured implements Tool { /** * @author Edison Chou * @version 1.0 */ public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, LongWritable> { public static final int K = 100; private TreeMap<Long, Long> tm = new TreeMap<Long, Long>(); protected void map( LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { try { long temp = Long.parseLong(value.toString().trim()); tm.put(temp, temp); if (tm.size() > K) { //tm.remove(tm.firstKey()); // 如果是求topk个最小的那么使用下面的语句 tm.remove(tm.lastKey()); } } catch (Exception e) { context.getCounter("TopK", "errorLog").increment(1L); } }; protected void cleanup( org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { for (Long num : tm.values()) { context.write(NullWritable.get(), new LongWritable(num)); } }; } /** * @author Edison Chou * @version 1.0 */ public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable> { public static final int K = 100; private TreeMap<Long, Long> tm = new TreeMap<Long, Long>(); protected void reduce( NullWritable key, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> values, Reducer<NullWritable, LongWritable, NullWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { for (LongWritable num : values) { tm.put(num.get(), num.get()); if (tm.size() > K) { //tm.remove(tm.firstKey()); // 如果是求topk个最小的那么使用下面的语句 tm.remove(tm.lastKey()); } } // 按降序即从大到小排列Key集合 for (Long value : tm.descendingKeySet()) { context.write(NullWritable.get(), new LongWritable(value)); } }; } // 输入文件路径 public static String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://hadoop-master:9000/testdir/input/seq100w.txt"; // 输出文件路径 public static String OUTPUT_PATH = "hdfs://hadoop-master:9000/testdir/output/topkapp"; @Override public int run(String[] args) throws Exception { // 首先删除输出路径的已有生成文件 FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(new URI(INPUT_PATH), getConf()); Path outPath = new Path(OUTPUT_PATH); if (fs.exists(outPath)) { fs.delete(outPath, true); } Job job = new Job(getConf(), "TopKNumberJob"); // 设置输入目录 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(INPUT_PATH)); // 设置自定义Mapper job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class); // 设置自定义Reducer job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class); // 设置输出目录 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(OUTPUT_PATH)); return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1; } public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); // map端输出启用压缩 conf.setBoolean("mapred.compress.map.output", true); // reduce端输出启用压缩 conf.setBoolean("mapred.output.compress", true); // reduce端输出压缩使用的类 conf.setClass("mapred.output.compression.codec", GzipCodec.class, CompressionCodec.class); try { int res = ToolRunner.run(conf, new MyTopKNumJob(), args); System.exit(res); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(4)实现效果:图片大小有限,这里只显示了前12个;
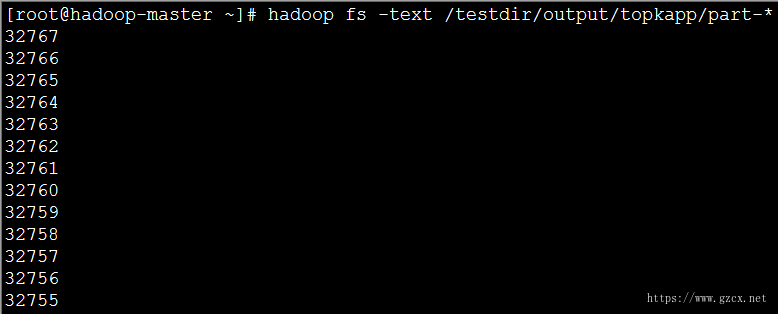
虽然例子很简单,业务也很简单,但是我们引入了分布式计算的思想,将MapReduce应用在了最值问题之中,也算是一个进步了。