如何让多个不同类型的后端网站用一个nginx进行反向代理实际场景分析
前段时间公司根据要求需要将聚石塔上服务器从杭州整体迁移到张家口,刚好趁这次机会将这些乱七八糟的服务器做一次梳理和整合,断断续续一个月迁移完
成大概优化掉了1/3的机器,完成之后遇到了一些问题,比如曾今零零散散部署在生产上一些可视化UI:apollo,kibana,grafana,jenkins 等等要么采用80端口,要
么对公开放了其他端口,为了安全,现在不再开放非80之外的公网端口,由于机器少了,80端口不够,这些可视化UI不再能直接访问到了。所以需另寻其他出路。
一:用nginx做反向代理
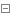
为了解决这两个问题,自然第一反应想到的就是使用反向代理,我的理想构思下应该是下图这样的。
既用户所有的请求都经过nginx,让nginx来判断当前url需要跳转到哪一个后端代理上,比较好的策略应该是让nginx来判断当前的host是什么来决定跳转到后端
的哪一个webserver上,比如a.mip.com 就跳转到apollo,j.mip.com 就跳转到jenkins. 以此类推,这样就可以完美解决了,是吧? 在nginx中你完全可以使用rewrite
模块下if指令来进行判断。
二:使用if指令
这里要提一下,nginx比较原始化,如果需使用第三方module,你还需要重新编译nginx,用起来很麻烦,所以这里干脆使用OpenResty,它扩展了nginx,并且
集成了很多成熟的lua模块,自行下载最新的1.15.8,安装方式和nginx一模一样。
默认是安装到/usr/local/目录下,当你看到有一个openresty目录表示你安装成功。
[root@localhost local]# ls bin etc games include lib lib64 libexec openresty sbin share src [root@localhost local]# pwd /usr/local
接下来你可以使用 nginx -v 来看一下openresty版本号啥的。
[root@localhost sbin]# pwd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin [root@localhost sbin]# [root@localhost sbin]# ./nginx -v nginx version: openresty/1.15.8.1
为了方便,我就直接使用nginx开启三个server:
<1> 192.168.23.129:80 nginx上开启的第一个网站,就是proxy了。
<2> 192.168.23.129:8001 nginx上开启的第二个网站,模拟apollo。
<3> 192.168.23.129:8002 nginx上开启的第三个网站,模拟jenkins。
1. apollo的模拟:
server { listen 8001; server_name somename alias another.alias; location / { root html; index apollo.html; } }
8001端口网站的默认页是apollo.html,这个apollo.html所在路径就是在nginx下的html目录,如下所示。
[root@localhost html]# pwd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html [root@localhost html]# ls 50x.html apollo.html index.html jenkins.html
2. jenkins的模拟
server { listen 8002; server_name somename alias another.alias; location / { root html; index jenkins.html; } }
jenkins.html的文件所在路径如上所示哈。不再赘述。
3. proxy的模拟
server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location / { if ($host = "a.mip.com") { proxy_pass http://localhost:8001; } if ($host = "j.mip.com") { proxy_pass http://localhost:8002; } }
可以看到,只需要使用rewrite模块下的if条件语句,通过$host系统变量判断当前的url中的host的值跳转到相应的网站。
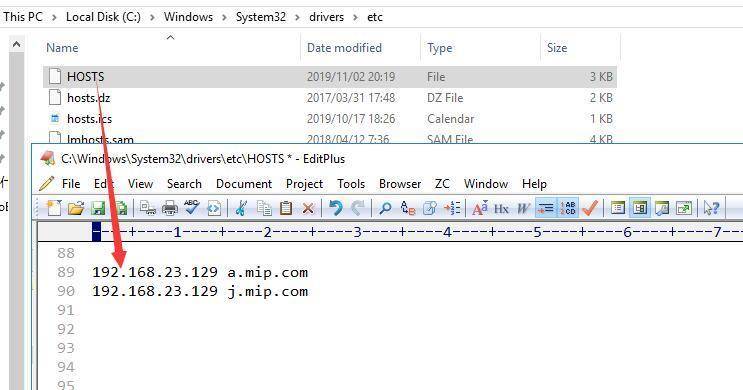
4. host映射
好了,接下来只需要将a.mip.com 和 j.mip.com 映射到nginx的ip地址192.168.23.129即可。因为这些域名方便记忆而不是真实存在的。
192.168.23.129 a.mip.com 192.168.23.129 j.mip.com
5. 启动nginx
[root@localhost sbin]# ./nginx [root@localhost sbin]# [root@localhost sbin]# [root@localhost sbin]# netstat -tlnp Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8001 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3802/nginx: master tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8002 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3802/nginx: master tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3802/nginx: master tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1172/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1724/master tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1172/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1724/master
通过上图可以看到,80,8001,8002 端口都已经开启了,接下来大家可以到浏览器去验证一下了。
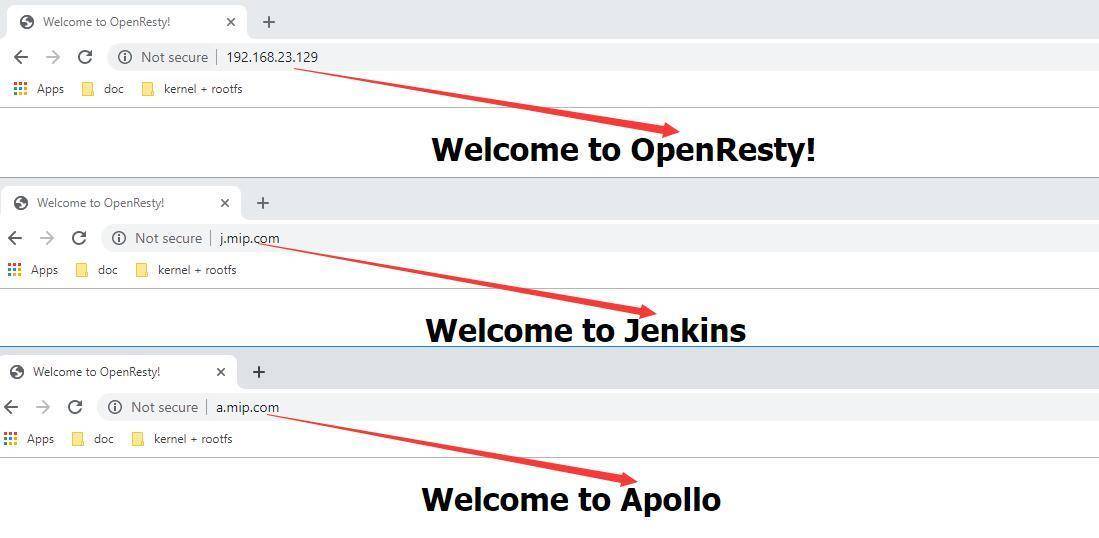
可以看到这个问题已经很完美的解决了,好了,这就是本篇和大家聊到的实际场景中遇到的一个问题,希望本篇对你有帮助,以下是全部的nginx.conf。
#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main '$host ----> $remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; # location = /get { # set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; # this requires ngx_set_misc # redis2_query get $key; # redis2_pass 10.105.13.174:6379; # } location / { if ($host = "a.mip.com") { proxy_pass http://localhost:8001; } if ($host = "j.mip.com") { proxy_pass http://localhost:8002; } root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # server { listen 8001; server_name somename alias another.alias; location / { root html; index apollo.html; } } server { listen 8002; server_name somename alias another.alias; location / { root html; index jenkins.html; } } # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }