几道常见的链表算法题
- 1. 两数相加
- 题目描述
- 问题分析
- Solution
- 2. 翻转链表
- 题目描述
- 问题分析
- Solution
- 3. 链表中倒数第k个节点
- 题目描述
- 问题分析
- Solution
- 4. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 问题分析
- Solution
- 5. 合并两个排序的链表
- 题目描述
- 问题分析
- Solution
1. 两数相加
题目描述
Leetcode:给定两个非空链表来表示两个非负整数。位数按照逆序方式存储,它们的每个节点只存储单个数字。将两数相加返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
问题分析
Leetcode官方详细解答地址:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/solution/
要对头结点进行操作时,考虑创建哑节点dummy,使用dummy->next表示真正的头节点。这样可以避免处理头节点为空的边界问题。
我们使用变量来跟踪进位,并从包含最低有效位的表头开始模拟逐 位相加的过程。
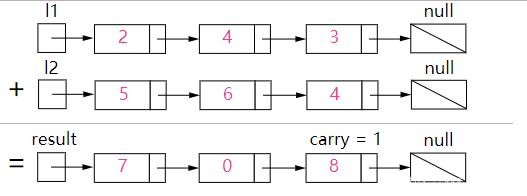
Solution
我们首先从最低有效位也就是列表 l1和 l2 的表头开始相加。注意需要考虑到进位的情况!
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/description/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, curr = dummyHead;
//carry 表示进位数
int carry = 0;
while (p != null || q != null) {
int x = (p != null) ? p.val : 0;
int y = (q != null) ? q.val : 0;
int sum = carry + x + y;
//进位数
carry = sum / 10;
//新节点的数值为sum % 10
curr.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr.next;
if (p != null) p = p.next;
if (q != null) q = q.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
curr.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
2. 翻转链表
题目描述
剑指 offer:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出链表的所有元素。
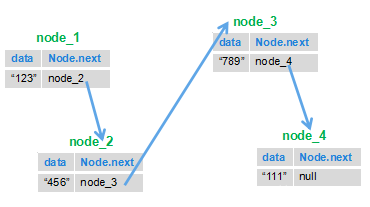
问题分析
这道算法题,说直白点就是:如何让后一个节点指向前一个节点!在下面的代码中定义了一个 next 节点,该节点主要是保存要反转到头的那个节点,防止链表 “断裂”。
Solution
```java public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } } ```
```java /* * * @author Snailclimb * @date 2018年9月19日 * @Description: TODO / public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode next = null;
ListNode pre = null;
while (head != null) {
// 保存要反转到头的那个节点
next = head.next;
// 要反转的那个节点指向已经反转的上一个节点(备注:第一次反转的时候会指向null)
head.next = pre;
// 上一个已经反转到头部的节点
pre = head;
// 一直向链表尾走
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
} ```
测试方法:
```java public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode a = new ListNode(1);
ListNode b = new ListNode(2);
ListNode c = new ListNode(3);
ListNode d = new ListNode(4);
ListNode e = new ListNode(5);
a.next = b;
b.next = c;
c.next = d;
d.next = e;
new Solution().ReverseList(a);
while (e != null) {
System.out.println(e.val);
e = e.next;
}
} ```
输出:
5
4
3
2
1
3. 链表中倒数第k个节点
题目描述
剑指offer: 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
问题分析
链表中倒数第k个节点也就是正数第(L-K+1)个节点,知道了只一点,这一题基本就没问题!
首先两个节点/指针,一个节点 node1 先开始跑,指针 node1 跑到 k-1 个节点后,另一个节点 node2 开始跑,当 node1 跑到最后时,node2 所指的节点就是倒数第k个节点也就是正数第(L-K+1)个节点。
Solution
```java /* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
// 时间复杂度O(n),一次遍历即可 // https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&tqId=11167&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking public class Solution { public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) { // 如果链表为空或者k小于等于0 if (head == null || k <= 0) { return null; } // 声明两个指向头结点的节点 ListNode node1 = head, node2 = head; // 记录节点的个数 int count = 0; // 记录k值,后面要使用 int index = k; // p指针先跑,并且记录节点数,当node1节点跑了k-1个节点后,node2节点开始跑, // 当node1节点跑到最后时,node2节点所指的节点就是倒数第k个节点 while (node1 != null) { node1 = node1.next; count++; if (k < 1) { node2 = node2.next; } k--; } // 如果节点个数小于所求的倒数第k个节点,则返回空 if (count < index) return null; return node2;
} } ```
4. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
Leetcode:给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
``` 给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
```
说明:
给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
该题在 leetcode 上有详细解答,具体可参考 Leetcode.
问题分析
我们注意到这个问题可以容易地简化成另一个问题:删除从列表开头数起的第 (L - n + 1)个结点,其中 L是列表的长度。只要我们找到列表的长度 L,这个问题就很容易解决。
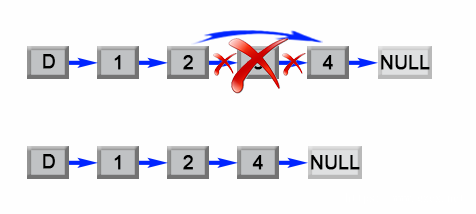
Solution
两次遍历法
首先我们将添加一个 哑结点 作为辅助,该结点位于列表头部。哑结点用来简化某些极端情况,例如列表中只含有一个结点,或需要删除列表的头部。在第一次遍历中,我们找出列表的长度 L。然后设置一个指向哑结点的指针,并移动它遍历列表,直至它到达第 (L - n) 个结点那里。我们把第 (L - n)个结点的 next 指针重新链接至第 (L - n + 2)个结点,完成这个算法。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 哑结点,哑结点用来简化某些极端情况,例如列表中只含有一个结点,或需要删除列表的头部
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
// 哑结点指向头结点
dummy.next = head;
// 保存链表长度
int length = 0;
ListNode len = head;
while (len != null) {
length++;
len = len.next;
}
length = length - n;
ListNode target = dummy;
// 找到 L-n 位置的节点
while (length > 0) {
target = target.next;
length--;
}
// 把第 (L - n)个结点的 next 指针重新链接至第 (L - n + 2)个结点
target.next = target.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 O(L) :该算法对列表进行了两次遍历,首先计算了列表的长度 LL 其次找到第 (L - n)(L−n) 个结点。 操作执行了 2L-n2L−n 步,时间复杂度为 O(L)O(L)。
- 空间复杂度 O(1) :我们只用了常量级的额外空间。
进阶——一次遍历法:
**链表中倒数第N个节点也就是正数第(L-N+1)个节点。
其实这种方法就和我们上面第四题找“链表中倒数第k个节点”所用的思想是一样的。基本思路就是: 定义两个节点 node1、node2;node1 节点先跑,node1节点 跑到第 n+1 个节点的时候,node2 节点开始跑.当node1 节点跑到最后一个节点时,node2 节点所在的位置就是第 (L-n ) 个节点(L代表总链表长度,也就是倒数第 n+1 个节点)
```java /* * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } / public class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
// 声明两个指向头结点的节点
ListNode node1 = dummy, node2 = dummy;
// node1 节点先跑,node1节点 跑到第 n 个节点的时候,node2 节点开始跑
// 当node1 节点跑到最后一个节点时,node2 节点所在的位置就是第 (L-n ) 个节点,也就是倒数第 n+1(L代表总链表长度)
while (node1 != null) {
node1 = node1.next;
if (n < 1 && node1 != null) {
node2 = node2.next;
}
n--;
}
node2.next = node2.next.next;
return dummy.next;
} } ```
5. 合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
剑指offer:输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
问题分析
我们可以这样分析:
- 假设我们有两个链表 A,B;
- A的头节点A1的值与B的头结点B1的值比较,假设A1小,则A1为头节点;
- A2再和B1比较,假设B1小,则,A1指向B1;
- A2再和B2比较 就这样循环往复就行了,应该还算好理解。
考虑通过递归的方式实现!
Solution
递归版本:
```java /* public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
//https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d8b6b4358f774294a89de2a6ac4d9337?tpId=13&tqId=11169&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
list1.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}else{
list2.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
```













